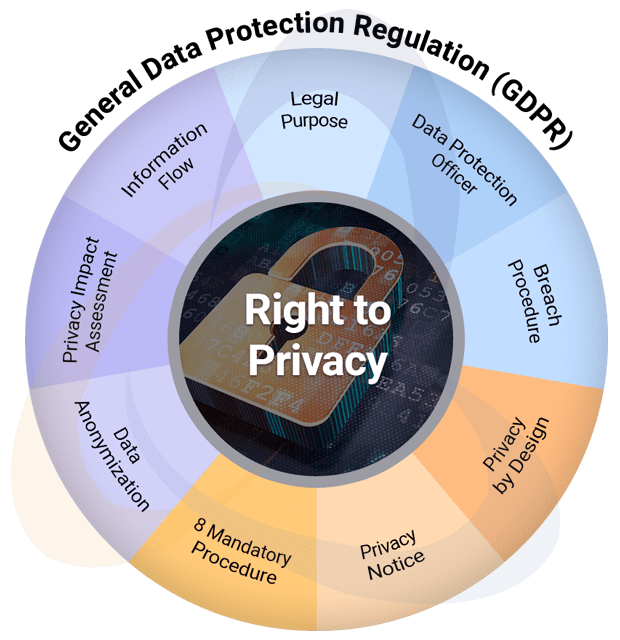
The right to privacy is an individual’s right to control their personal information and protect it from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure. It ensures autonomy, dignity, and freedom from intrusion across digital, physical, and informational spaces.
GDPR is the EU’s data protection law that governs how organisations collect, use, store, and share personal data. Businesses must ensure lawful processing, obtain valid consent, protect data with strong security, honour individual rights, maintain transparency, report breaches promptly, and demonstrate compliance through documented policies, safeguards, and accountability measures.
Coral has advised clients on GDPR since the regulation’s inception in 2018, guiding organisations through a comprehensive consulting journey that strengthens privacy processes, avoids costly mistakes, and builds a mature, audit-ready compliance program aligned with regulatory expectations.
Questions and clarifications on GDPR scope, implementation or audit? Please get in touch with us for a no-obligation conversation.